Diffusion of Innovations the process by which an innovation is communicated through certain channels over time among the members of a social system. It is a theory that seeks to explain how, why, and at what rate new ideas and technology spread through cultures. An innovation is an idea, behaviour, or object that is perceived as new by its audience.
Four Main Elements in the Diffusion of Innovations
- The innovation: An idea, practice, or object perceived as new by an individual or other unit of adoption
- Communication channels: Means by which messages get from one individual to another
- Time:It is involved in diffusion in three ways;
1- Innovation-diffusion process:
- Knowledge
- Persuasion
- Decision
- Implementation
- Confirmation
2-Innovativeness: The degree to which an individual or other unit of adoption is relatively earlier in. The innovation must be widely adopted in order to selfsustain. There are five different adopters on the basis of their innovativeness.
Innovators :Innovators are willing to take risks, have the highest social status, have financial liquidity, are social and have closest contact to scientific sources and interaction with other innovators.
Early Adopters: These individuals have the highest degree of opinion leadership among the adopter categories. Early adopters have a higher social status, financial liquidity, advanced education and are more socially forward than late adopters. They are more discreet in adoption choices than innovators
Early Majority :They adopt an innovation after a varying degree of time that is significantly longer than the innovators and early adopters. Early Majority have above average social status, contact with early adopters and seldom hold positions of opinion leadership in a system
Late Majority: They adopt an innovation after the average participant. These individuals approach an innovation with a high degree of skepticism and after the majority of society has adopted the innovation. Late Majority are typically skeptical about an innovation, have below average social status, little financial liquidity, in contact with others in late majority and early majority and little opinion leadership.
Laggards: They are the last to adopt an innovation. Unlike some of the previous categories, individuals in this category show little to no opinion leadership. They usually have the şlowest social status, lowest financial liquidity, oldest among adopters, and in contact with only family and close friends
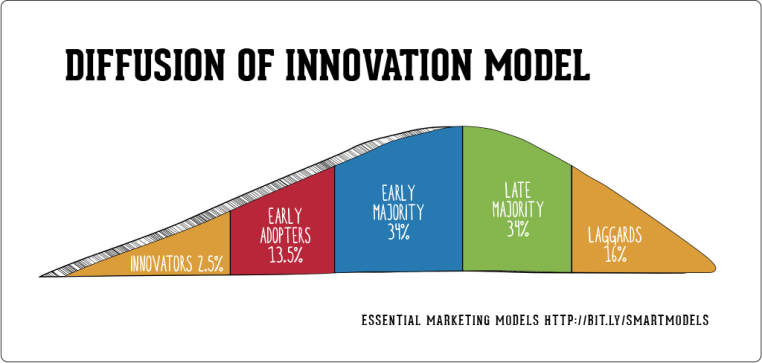
3- Innovation’s rate of adoption: The relative speed with which an innovation is adopted by members of a social system
- Social system: A set of interrelated units that are engaged in joint problem solving to accomplish a common goal.

Leave a comment